미래의 중소기업과 남북 경제협력
 등록일 / 수정일
등록일 / 수정일 페이지 / 형식
페이지 / 형식 자료평가
자료평가 구매가격
구매가격
- 2019.05.13 / 2019.05.13
- 28페이지 /
 ppt (파워포인트 2003)
ppt (파워포인트 2003) - 평가한 분이 없습니다. (구매금액의 3%지급)
- 800원
최대 20페이지까지 미리보기 서비스를 제공합니다.
자료평가하면 구매금액의 3%지급!
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13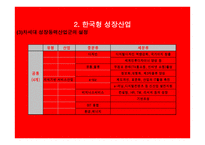 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20
추천 연관자료
- 본문내용
-
미래의 중소기업과 남북경제협력
제1절 미래 사회와 기업환경의 변화
제2절 미래의 성장 산업
제3절 미래 지식사회의 중소기업
제4절 예방경영전략의 모색
제5절 남북통일과 중소기업
제1절 미래 사회와 기업환경의 변화
제1절 미래 사회와 기업환경의 변화
미래 사회의 모습
거대한 글로벌 사회
상호주의 사회(공동체적 삶)
기업 간 제휴의 시대
기업의 구조조정 시대
디지털 사회(유비쿼터스)
삶의 질이 중요시 되는 사회(분배,형평,국제공조)
Customers face constant pressure to lower their cost of test. At the same time, their newest devices, often targeted for battery-powered applications, are more complex and have higher pin-counts. The latest components (such as ICs, RFICs, and SOCs) are pushing the limits of test system technology.
Higher pin-counts and more analog circuitry in devices require more SMU channels, so test system density is increasingly critical.
Todays more-complex devices require test systems to perform more tests in the same amount of time as testing required before.
The push to extend battery life requires a wide dynamic range. Low current measurements are critical to good battery life characterization and leakage measurements. Power supplies are unable to provide these measurements.
The lack of optimized test solutions for multi-channel source-measure applications has forced manufacturers to choose among bulky, overpriced mainframe-based systems, slow instrument-based systems using PC control, or fast instrument-based systems that are extremely complex to develop.
제1절 미래 사회와 기업환경의 변화
2. 미래 기업환경의 변화
제조기술의 변화 (소형화, 경량화)
무형자산의 시대 (제품 유형보다는 정보,서비스, 컨텐츠)
제조업의 양극화 현상(초거대기업, 탈지역화)
인본주의 경향의 강화(자연 친화적, 인간중심적)
소비자욕구의 변화
(대량생산체제지속상류층, 다품종소량생산 중산,서민층)
지식,정보,기술사회의 가속화(한국의 미래결정)
Customers face constant pressure to lower their cost of test. At the same time, their newest devices, often targeted for battery-powered applications, are more complex and have higher pin-counts. The latest components (such as ICs, RFICs, and SOCs) are pushing the limits of test system technology.
Higher pin-counts and more analog circuitry in devices require more SMU channels, so test system density is increasingly critical.
Todays more-complex devices require test systems to perform more tests in the same amount of time as testing required before.
The push to extend battery life requires a wide dynamic range. Low current measurements are critical to good battery life characterization and leakage measurements. Power supplies are unable to provide these measurements.
The lack of optimized test solutions for multi-channel source-measure applications has forced manufacturers to choose among bulky, overpriced mainframe-based systems, slow instrument-based systems using PC control, or fast instrument-based systems that are extremely complex to develop.
제1절 미래 사회와 기업환경의 변화
3. 미래 소비자욕구의 변화
속도화와 편리화 추구(속도의 경제, 편리의 문명)
감성의 중시
(미적, 감성적,패션화 진행, 휴먼터치형 상품, 제품과 서비스의 체험을 구매)
다양화 (소비자의 욕구)
스마트소비 (정보수집,전문가집단 의존,리스,렌털)
Customers face constant pressure to lower their cost of test. At the same time, their newest devices, often targeted for battery-powered applications, are more complex and have higher pin-counts. The latest components (such as ICs, RFICs, and SOCs) are pushing the limits of test system technology.
Higher pin-counts and more analog circuitry in devices require more SMU channels, so test system density is increasingly critical.
Todays more-complex devices require test systems to perform more tests in the same amount of time as testing required before.
The push to extend battery life requires a wide dynamic range. Low current measurements are critical to good battery life characterization and leakage measurements. Power supplies are unable to provide these measurements.
The lack of optimized test solutions for multi-channel source-measure applications has forced manufacturers to choose among bulky, overpriced mainframe-based systems, slow instrument-based systems using PC control, or fast instrument-based systems that are extremely complex to develop.
제2절 미래의 성장산업
자료평가
-
아직 평가한 내용이 없습니다.