[정치학] 지역주의 쇠퇴와 사회균열-대통령 선거와 정당 정치 사례를 중심으로(영문)
 등록일 / 수정일
등록일 / 수정일 페이지 / 형식
페이지 / 형식 자료평가
자료평가 구매가격
구매가격
- 2011.12.05 / 2019.12.24
- 17페이지 /
 docx (MS워드 2007이상)
docx (MS워드 2007이상) - 평가한 분이 없습니다. (구매금액의 3%지급)
- 1,700원
최대 20페이지까지 미리보기 서비스를 제공합니다.
자료평가하면 구매금액의 3%지급!
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4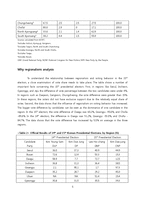 5
5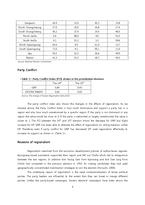 6
6 7
7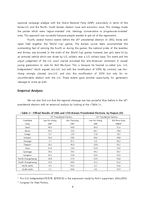 8
8 9
9 10
10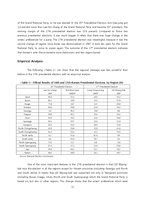 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17
추천 연관자료
- 목차
-
1. Introduction
(including methodology and political background of regionalism)
2. The 15th presidential election
3. The 16th presidential election
4. The 17th presidential election
5. Conclusion
6. References
7. The report about the team performance
- 본문내용
-
Development of regionalism and political background
Antagonism between Kyongsang province and Cholla province had already been formed under the Kyongsang based former presidents Park Chung-Hee, Chun Doo-Hwan and Roh Tae-Woo. While Kyongsang province developed including the establishment of industry facilities, Cholla province remained underdeveloped compared to Kyongasang province. Regionalism had existed during authoritarian rule but it can’t be considered as a social cleavage because it wasn’t structuralized determining the party system of South Korea.
South Korea’s regionalism was triggered when the nation was democratized in 1987 after the authoritarian regime collapsed. Under the authoritarian rule, many civilian leaders cooperated to fight for democracy against the military dictatorship. However, once democracy was achieved each opposition leader created their own party in order to prepare for the upcoming presidential elections. Two rival politicians at the time were Kyongsang province based Kim Young Sam and Cholla province based Kim Dae-Jung. In addition, the fact that the nation was finally democratized overcoming the long tenure of authoritarian rule and that it was a direct presidential election system in 16 years since April 27th 1971 elections, enhanced the citizens’ eagerness to vote.
Given this situation, the two political leaders chose to utilize regionalism as their election strategy or campaign vehicles. Each party created by the two leaders saw regional cleavage as a strong resource they could mobilize in order to gain support and win the 13th presidential election. All efforts were exerted to gain votes from each provinces and this election created the base for the regional cleavage to root deeply in Korean politics and voting behaviors of citizens. This cleavage structure formed by regionalism were strengthened and expressed at the following general elections and presidential elections.
2. The 15th Presidential Election and the regional cleavage
Election background
The 15th presidential election can be seen as a turning point in Korea. Periodically, the election opened the way to the 21st century and historically, the election had the potential to change political forces and make a smooth transition to a new regime. Most importantly, the election was during a time of economic hardship. After long years of development, Korea was catching up to the wealthy, developed nations and accepted to OECD. However, the ambitious financial liberalization of president Kim Young Sam had failed miserably. Some scholars claim that the reform had failed due to the absence of the state intervention and supervision. Regardless of the cause, the reform had failed and the Korean economy collapsed. Foreign capital outflow was rapid and short term loans couldn’t be solved. The government announced its economic failure and the IMF came in to restructure the economy according to the Anglo-American model (Jeong, 1998).
- 참고문헌
-
- The 1997 presidential election in South Korea. (Kang, Won-Taek and Hoon Jaung, 1999, Electoral Studies. Vol. 18, Issue 4 pp. 599-608)
- The Presidency, Regionalism, and Distributive Politics in South Korea. (Horiuchi, Yusaku and Seungjoo Lee, 2008, Comparative Political Studies. Vol. 41, No. 6 pp. 861-882)
- The 15th Presidential Election, Kim Dae-jung government, and the democracy (Jeong Young-Tae, 1998, Economy and Society Vol. 37, pp. 202-223)
- Elections and Regionalism in Korea (Nam Kook-chan, 2010, Incheon University, Graduate School of political science)
- The Splits and Mergers of Korean Parties and Instability of Party System (Kwak Jin-young, 2009, Konkuk University)
- The Change of Korean Regionalism: A View on Voting Behaviors and Political Parties (KIM, Jin Ha, 2010, Kelmyung University,)
- The Changing Korean Party System and the Regionalism? (Kang Myoungsei, 2005, Sejong Institute)
- Effects of Social and Ideological Cleavages on Vote Choice in the Korean Presidential Election of December 19, 2007 (Park Chan-wook, 2009, Seoul National University)
- 2002 Presidential election and the changes in the structure of political parties (Kim, Yong-bok, 2002, Critical Sociology seminar, Nurimedia)
- The changes in the political party system in South Korea in terms of Realignment (Lee Jung-jin, Suwon Science University)
- A study of Major Parties Pledges in the 16th Presidential Election (Ahn Chul-hyun, 2003, Kyung-sung University)
- How should we look at the all-in support votes of Honam? (Ju Gook-jeon, Moonsung Middle School Teacher, 2002, Nurimedia)
- Presidential Election and Regional Cleavage in Korea: Focused on the 15~17th presidential election in the capital area (Kim YoungTae, 2009, Mokpo National University)
- A Multiple Indicators Approach of Partisan Attitudes: An Analysis of the Effect of Partisanship on Voters’ Choice in the 17th Presidential Election in Korea (Hwang AhRan, 2008, Pusan National University)
- The Effect of President Roh’s Approval Rating on the 2007 Presidential Election (Ka Sanjoon, Dankook University)
- Cleavage Structure and Party System: Regionalism, Ideology, and the 2007 Korean Presidential Election (Cho SungDai, 2008, Hanshin University)
자료평가
-
아직 평가한 내용이 없습니다.
오늘 본 자료
더보기

최근 판매 자료
- 사회복지 공급주체에서 국가공급과 민간공급의 특징 및 장단점을 설명하고 최근 한국의 사회서비스산업 민영화 및 시장화에 대한 생각을 논하시오
- [사회복지정책론] 사회복지정책의 보편주의와 선별주의적 개념을 비교하여 설명하고 장단점에 따른 정책적 대안을 작성하시오
- 공공기관과 민간기관이 차지하는 사회적 영향력을 순기능적인 입장과 역기능적인 입장에서 토론해 보세요
- 비평적감상문_디카시_이렇게 읽고 쓴다
- 사회복지의 공급주체에서 국가공급(공급)과 민간공급의 특징 및 장단점을 설명하고 최근 한국의 사회서비스사업 민영화 및 시장화에 대한 생각을 논하시오
- 고부갈등 정의,원인,유형,특징과 극복사례연구 및 고부갈등 문제점과 해결방안제시 및 나의의견정리 - 고부갈등 연구레포트
- 자립생활의 정의와 특성, 원리및 기본철학을 설명하시오 자립생활 서비스의 내용에 대해 설명하고, 그 중에 가장 중요하다고 생각하는 서비스는 무엇인지 논하시오
- 유아와 조부모 특징, 유아와 관련하여 조부모와 상담시 유의해야 할 점, 다루어야 할 점에 대해 서술하시오
- 지그문트 프로이트의 정신분석이론의 내용을 요약, 정리하고 프로이트가 개인의 성격이 5년 이내에 결정된다고 주장한 결정론적 입장을 정리 후 학습자의 의견을 제시하시오
- 베이커리 카페 사업계획서
저작권 관련 사항 정보 및 게시물 내용의 진실성에 대하여 레포트샵은 보증하지 아니하며, 해당 정보 및 게시물의 저작권과 기타 법적 책임은 자료 등록자에게 있습니다. 위 정보 및 게시물 내용의 불법적 이용, 무단 전재·배포는 금지됩니다. 저작권침해, 명예훼손 등 분쟁요소 발견시 고객센터에 신고해 주시기 바랍니다.